This dynamic nature of choices means that you can craft a place to suit your precise market view. Maybe there’s a giant Federal Reserve assembly developing and also you count on the market to overreact, however you don’t have a selected view as to which path. On this case, you should utilize a market-neutral choice unfold like a straddle or strangle.
In the identical vein, if the monetary media and merchants are making a giant stink about one thing you deem a nothingburger, you should utilize strangles or straddles to take the view that the market will underreact to the information in comparison with what the market pricing expects.
Strangles and straddles are market-neutral choices spreads that are apathetic to the path that value strikes. They as an alternative enable a dealer to specific a view on the magnitude of the value transfer, regardless if the value strikes up or down.
Let’s paint a fast hypothetical for demonstration.
There’s a Federal Reserve assembly in per week. There’s tons of discuss the potential of a Fed pivot and the dramatic implications that’d have for the worldwide economic system. Wanting on the S&P 500 choices for that expiration, you see that the implied volatility could be very excessive in comparison with previous Fed conferences. Merchants expect the Fed to drop a shock in some sense.
Based mostly by yourself macro view, you’re unconvinced. You consider the Fed will proceed their marketing campaign of modest hikes of charges by the primary half the yr. In different phrases, you count on enterprise as traditional whereas the market expects radical change.
As an choices dealer, you’re absolutely conscious that change equals volatility and the dearth of change leads volatility to contract, making most choices expire nugatory. You determine to promote a straddle, which includes promoting an at-the-money put and an at-the-money name concurrently. Ought to your view pan out, you’ll have the ability to pocket a superb portion of the premium you collected if you opened the commerce.
What Is a Strangle?
A strangle is market-neutral choices unfold that includes the simultaneous buy or sale of an out-of-the-money name and an out-of-the-money put. So if the underlying is buying and selling at $20.00, you would possibly purchase the $18 strike put and the $22 strike name.
On this case, you’re hoping for a big value transfer in both path, as your break-even value is usually fairly removed from the present underlying value.
Let’s take a look at a quick instance of a lengthy strangle in $SPY utilizing a .30 delta put and name with 27 days to expiration. Right here’s the choices we’re shopping for:
● SPY (underlying) value: 396.00
● 1 386 FEB 27 PUT @ 4.31 (-0.30 delta)
● 1 407 FEB 27 CALL @ 3.54 (0.30 delta)
● Value of Place: 7.85
Right here’s the payoff diagram of this place:
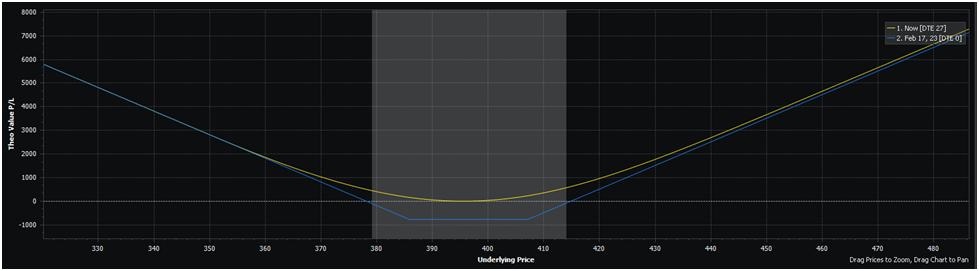
As soon as the place will get outdoors of the shaded grey space, the place is in-the-money. To supply some context to this place, SPY should transfer up or down roughly 4.5% to your place to be in-the-money.
Let’s take a look at the identical commerce however from the quick facet:
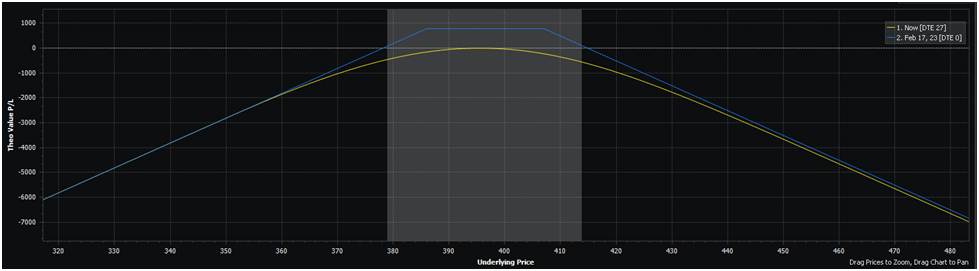
The main points of this commerce are a mirror reverse of the earlier instance. You’d gather a $7.85 credit score, and your break-even ranges are outdoors of the shaded grey space. You’d make this commerce if you happen to count on SPY to stay inside that vary by expiration (27 days).
Strangle Strike Choice
Strike choice is a major issue right here and there’s no right reply actually.
The decrease delta choices you select, the cheaper the unfold and the decrease the chance of revenue shall be. Maybe you have got a really particular market view, making strike choice apparent. However normally, novice choice merchants select arbitrary strikes, which is a mistake. Strike choice is without doubt one of the most vital points of commerce structuring.
A simple solution to begin being extra considerate about deciding on strikes is to view an choice’s delta as a tough approximation of the chance of expiring in-the-money. This straightforward trick offers plenty of context to choice pricing.
You’ll see at-the-money choices typically hover round .50 delta, as a result of the market mainly has a 50/50 probability of going up or down over any time interval not measured in years. As you get farther from the cash, deltas go down, which additionally makes intuitive sense.
Utilizing this framework, you’ll be able to take a look at a .20 delta strangle and suppose “the market thinks there’s a 20% probability of both of those choices expiring in-the-money. Is my chance forecast greater or decrease than that? If you happen to can reply this query, your strike choice turns into not solely simpler, however way more considerate.
What’s a Straddle?
A straddle is a market-neutral choices unfold involving the simultaneous buy (or sale) of a name and put on the similar strike value and expiration. The purpose of the commerce is to make a wager on volatility in a market-neutral style.
Whereas any commerce commerce involving shopping for or promoting a put and a name on the similar strike value and expiration is technically a straddle, the vast majority of the time once we discuss straddles, we’re speaking about an at-the-money straddle, which means you purchase a put and name on the ATM strike.
In different phrases, if implied volatility is 20%, however you count on future realized volatility to be a lot greater than that, shopping for a straddle would supply a revenue no matter which path the market goes, or the way it arrives there.
Alongside comparable strains, if you happen to count on realized volatility to be far lower than 20%, you’ll be able to quick a straddle to revenue from the market’s overestimation of volatility.
In a phrase, you need to purchase a protracted straddle if you suppose choices are too low-cost, and quick straddles or quick strangles when choices appear too costly.
Right here’s an instance of a lengthy straddle in SPY with 27 days to expiration. With SPY buying and selling at 396 on the time of writing, we’d need to purchase the 396 name and places. Right here’s how that’d look:
● SPY (underlying) at 396.00
● 1 396 FEB 27 CALL @ 8.59
● 1 396 FEB 27 CALL @ 7.69
● Whole price of commerce: $16.28
As you’ll be able to see, this ATM straddle prices greater than double what our 0.30 delta strangle prices us. Being flawed on straddles is way extra painful. However this payoff diagram reveals us the upside to this trade-off:
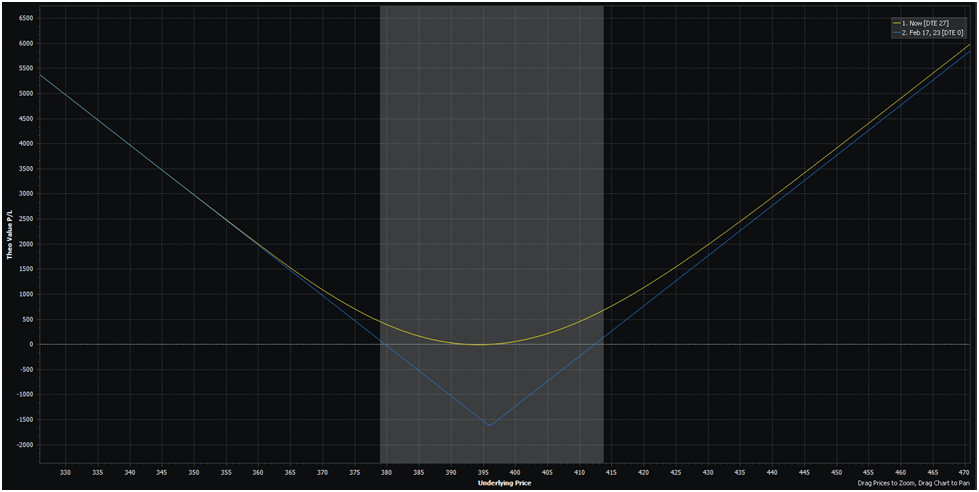
What’s most fascinating right here is that our 0.30 delta strangle from the earlier instance has practically equivalent break-even factors to this ATM straddle: round 379 and 414. Nevertheless, wanting on the form of the P&L, you’ll be able to see that you simply solely expertise your max P&L loss if the market goes completely nowhere and continues to be at 396 at expiration.
If the market strikes even modestly in both path, your commerce begins to maneuver in your favor. That is in stark distinction to our strangle, wherein we expertise most loss at a far wider vary of costs.
So when you do should shell out extra premium to determine a straddle, it’s fairly unlikely you’ll really lose your entire premium.
The Similarities Between a Strangle and a Straddle
-
Each are Outlined-Danger Choices Spreads
Each the straddle and strangle contain shopping for two completely different choices with out promoting any choices to offset the premium paid. So essentially the most you’ll be able to lose in both a straddle or strangle is the premium you paid.
A defining trait of many defined-risk, lengthy choices methods is the convexity afforded to you; you understand the utmost you’ll be able to lose is X, however your upside is theoretically limitless. This may after all result in occasional huge wins the place the market mainly developments in your path till expiration.
-
Each Are Market-Impartial
Choices will let you categorical a extra various array of market views than merely lengthy or quick. A type of is the power to revenue with out having to foretell the path of value.
Whereas market-neutral is a simple time period to make use of as a result of most perceive it off the bat, that’s not completely right. You’ll be able to extra precisely name straddles or strangles delta impartial technique as a result of when you’re impartial on the path of value, you’re nonetheless finally taking some form of market view.
Within the case of straddles and strangles, you’re taking a view on whether or not volatility will broaden or contract. Or in different phrases, do you have got conviction on whether or not the market will transfer kind of than the choice market thinks? In that case, you’ll be able to revenue from this view.
Put merely, if you happen to count on the underlying to get extra unstable earlier than expiration, you need to be lengthy volatility. Taking a protracted volatility view assumes that the choices market’s implied volatility forecast is simply too low, making choices too low-cost.
Expressing a protracted volatility view within the context of a straddle or strangle means taking the lengthy facet of the commerce (shopping for the choices as an alternative of shorting them).
Simply as we described within the intro of this text, if you happen to maintain the view that the market is overhyping the importance of a catalyst, you make the identical commerce in reverse; you’ll be able to quick an at-the-money put and an ATM name, which is a brief straddle. If realized volatility is decrease than implied volatility, you then’ll find yourself pocketing a superb portion of premium if you shut the commerce.
The Variations Between a Strangle and a Straddle
Straddles and strangles categorical very comparable views; merchants utilizing them are both expressing a protracted or quick volatility whereas remaining agnostic on value path. The place they differ is the magnitude of their view, or how flawed they suppose the market pricing of implied volatility is.
From the long-volatility perspective, it’s cheaper to purchase a strangle since you’re shopping for OTM choices however the dilemma is that with cheaper OTM choices, you have got a decrease chance of making the most of the commerce. The market wants to maneuver extra to place you within the cash.
If you happen to flip this dilemma to the quick facet, you have got the identical downside. When shorting strangles, you have got a excessive chance of gathering all the premium on the conclusion of the commerce, however when the market does make a giant transfer, you expertise an enormous loss. So you’ll be able to rack up a number of wins in a row solely to see one loss knock out all of those features.
ATM Straddles Have Extra Premium Than Strangles
At-the-money choices have extra premium than OTM choices. So it follows that the straddle, a ramification with two ATM choices, would have way more premium than one with two OTM choices, the strangle.
Because of this, systematic sellers of premium, what you would possibly name the “Tastytrade crowd,” actually like straddles for his or her excessive premium properties. This property of upper premium doesn’t make the straddle superior for premium sellers, as there’s no free lunch–premium sellers are paying for this greater stage of premium with a decrease win charge on their trades.
Straddles Have a Greater Likelihood of Revenue
As it’d’ve turn into clear all through this text, establishing choices spreads is all about tradeoffs. Wish to put out a small quantity of capital with the potential of an enormous win? You are able to do that, however you’ll hit on these trades a small portion of the time. Likewise, if you wish to revenue on most of your trades, you’re basically paying for that within the sense that your frequent winners shall be small income and your rare losers shall be a lot larger.
This dynamic applies equally to the selection between straddles and strangles. A straddle requires extra premium outlay with a better chance of profiting the commerce, whereas strangles allow you to danger much less general on the commerce, however you must be “extra proper” in your market view to make a revenue.
Your selection between these spreads if you need to make a market-neutral wager on volatility finally comes all the way down to your individual buying and selling temperament, in addition to which unfold makes extra sense given your market view.
Backside Line: Straddles and Strangles Are About Volatility
For many merchants, their introduction to choices is expounded to an attraction to the leverage and convexity for his or her directional market bets. However as they peel the layers away and be taught in regards to the true nature of choices, they be taught that they’re way over instruments to get leveraged publicity to a inventory or index.
The primary and best lesson is the time side. The longer-dated the choice, the extra it prices. Optionality prices cash. That is very straightforward to know. One-year choices ought to price greater than one-day choices.
The subsequent step is knowing how market volatility pertains to choice pricing. It’s far much less intuitive.
However, contemplate this hypothetical…
You’re supplied the selection between paying the identical value for a one-month at-the-money choice on two completely different shares.
One is extremely unstable and steadily swings 10% each day. Tesla (TSLA) is an efficient instance.
The second inventory is a steady blue chip inventory that doesn’t transfer round that a lot. Assume one thing like Walmart (WMT) as an illustration.
Most would appropriately select the unstable inventory. It’s frequent sense, proper? In any case, a inventory like Tesla can transfer up or down 30% in a month, whereas a inventory like Walmart typically swings lower than 10% in a month.
So like time, volatility has a value. However as a result of future volatility is unsure, that value is dynamic and topic to the opinion of the market. Like all market value, there are all the time opportunistic merchants who revenue from the inefficiencies of market pricing.
That is the place volatility buying and selling is available in. Consider strangles and straddles because the hammer and drill of volatility buying and selling. They’re basic instruments you attain for time and again.
Bear in mind, everytime you purchase or promote an choice, you’re making an implicit wager on volatility, whether or not you prefer it or not. If you happen to purchase an choice, you’re taking the stance that volatility is simply too low-cost.
Associated articles

